Mobile security is no longer just about antivirus apps or lock screen passwords. It’s an entire ecosystem of protocols, software updates, digital barriers, and hardware safeguards that determines who can access your data—and who can’t. Over the past few years, the gap between Android and iOS has narrowed somewhat when it comes to security, but key differences remain that affect just how secure your device really is.
Two Philosophies, Two Approaches to Protection
iOS: A Closed System with Strict Rules
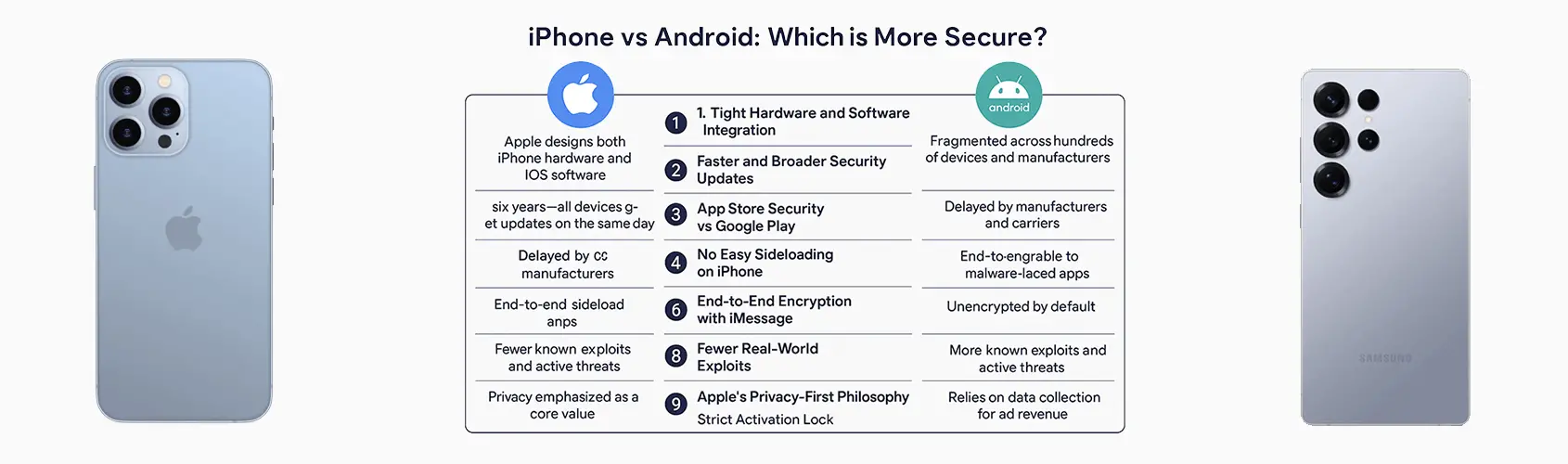
Apple has one major advantage up its sleeve: complete control over the entire process—from chip design to the operating system to the app store. This level of control allows Apple to enforce stringent security policies. The system is locked down, limiting app access to critical functions and using hardware like the Secure Enclave to protect sensitive data (such as Face ID or fingerprint information).
What does this mean in practice?
- Lower risk of malware, since apps can’t make it into the system without rigorous approval.
- Fast and long-term system updates (up to 7–8 years, even for older models).
- Strong protection against unauthorized tampering, since apps can’t access the system kernel or perform low-level modifications.
- User permissions are tightly restricted, which greatly reduces the risk of data misuse.
Apple also applies its security standards consistently across all models, which is not something that can be said for Android.
Android: Openness and Variability
Android offers more customization and freedom for users, but this comes with additional risks. While the base system is open-source, manufacturers like Samsung, Xiaomi, and OnePlus heavily modify it. This leads to:
- Updates dependent on the manufacturer (often only 2–5 years), leaving many older devices without critical security patches.
- The ability to install apps from unofficial sources (sideloading), which bypasses safeguards and introduces malware risks.
- Varying levels of hardware-based security—brands like Google (Titan M2) and Samsung (Knox) go the extra mile, while others rely on basic encryption.
Tech-savvy users often appreciate the flexibility and the ability to install custom ROMs. However, that freedom demands more vigilance.
App Security: App Store vs Google Play
App security is a major component of overall mobile protection. Apple uses a mix of automated and manual checks before apps are approved for its App Store. The process may be slower, but it significantly reduces the risk of malicious or scam apps getting through.
By contrast, Google Play leans more on automation and machine learning. While this allows them to handle large volumes of apps, it also means lower precision. Fake apps and clones of popular tools still appear, often disguised as harmless utilities or games.
Neither platform is perfect. Research has shown:
- Over 40% of children’s apps on Google Play violate COPPA rules.
- More than 25% of apps on the App Store also have privacy compliance issues.
Practical Differences in Data Protection
Biometrics and Secure Chips
- iOS: Secure Enclave is a separate part of the processor that protects biometric data (Face ID, Touch ID) and other sensitive information. Even the operating system doesn’t have direct access.
- Android: Protection varies by brand. Google uses the Titan M2 chip for verified boot and encryption protection. Samsung has its own Knox secure environment.
Device Locking and Encryption
Both systems support modern encryption protocols (like AES-256), biometric unlocking, remote data wiping, and more. Apple, however, deploys these features consistently across all devices. On Android, it depends on the manufacturer and specific device model.
Antivirus Protection
- Android allows third-party antivirus apps, which can provide real-time scanning, phishing protection, permission analysis, and more.
- iOS doesn’t offer the same access for antivirus apps. The system is designed to not require them—but that doesn’t mean it’s invincible. Jailbreaking or sideloading (now legal in the EU) can weaken iPhone defenses.
New Threats in 2025
As digital threats evolve, so do attack methods:
- Zero-click attacks: Malware that infects your phone without any user interaction. One poorly secured app or message is all it takes.
- Social engineering: The human factor remains the weakest link—attackers impersonate couriers, banks, or support staff.
- Artificial intelligence: AI helps detect threats, but hackers also use it—for example, deepfake audio scams are on the rise.
10 Tips to Stay Safe on Any Device
- Keep your system and apps updated—enable auto-updates if possible
- Install apps only from official sources—Google Play or App Store
- Use biometric authentication—combine fingerprint, face ID, and a strong passcode
- Strong, unique passwords—use a password manager with encryption
- Back up your data—be prepared for loss or ransomware attacks
- Use a VPN—encrypts your data on public Wi-Fi and prevents tracking
- Watch out for phishing attempts—don’t click on suspicious links or messages
- Restart your phone weekly—interrupts persistent attacks
- Review app permissions regularly—don’t grant unnecessary access
- Enable multi-factor authentication (2FA)—preferably via an authenticator app
Final Verdict: Which One Is Safer?
Both platforms aim to protect users, but they do so differently. iPhones stand out for centralized control, hardware-based protections, and extended software support. Android appeals to those who want more control—but that comes with added responsibility and risk.
Security isn’t black and white. If you’re cautious, both Android and iPhone can be very secure. But if you ignore updates and click on every pop-up ad, no device will protect you.
Ultimately, security is a mindset—whether you’re an Apple fan, an Android power user, or switch between both. In 2025, the difference between the two is smaller than ever, but iPhones remain safer out of the box, while Android gives you tools—you just have to use them wisely.